Start mapping with the Ouster-CLI
Installation
The Ouster CLI mapping functionality is a part of the Ouster SDK Python package.
To install the Ouster SDK with the mapping capabilities:
$ python3 install ouster-sdk
PS > py -3 install ouster-sdk
Mapping Tools
After installing the Ouster SDK and mapping dependencies, you can explore various mapping tools using a connected Ouster sensor or a PCAP/OSF file.
To explore and configure the parameters of the SLAM algorithm, you can use the --help flag
to view the available options.
ouster-cli source <SENSOR_HOSTNAME> / <FILENAME> slam --help
The slam command can be combined with either or both the save and viz commands.
You can further explore each command in detail by accessing their respective submenus
using the --help flag.
ouster-cli source <SENSOR_HOSTNAME> / <FILENAME> slam save --help
ouster-cli source <SENSOR_HOSTNAME> / <FILENAME> slam viz --help
SLAM Command
Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM) is a technique that enables a system to construct a map of its surroundings while simultaneously determining its own position on that map.
We use the slam algorithm to determine the lidar movement trajectory, correct motion distortion and reconstruct a detailed and precise point cloud map.
Connect to a sensor or use a PCAP/OSF file Download Sample PCAP File
Note
Connecting to an Ouster sensor is covered in the Networking Guide section of the Ouster Sensor Documentation.
Then execute the following command:
ouster-cli source <SENSOR_HOSTNAME> / <FILENAME> slam viz -e exit save sample.osf
Note
Please replace <HOSTNAME> with the corresponding hostname or IP of your sensor, and replace <FILENAME> with the actual file path and name of the PCAP/OSF file. Similarly, make the necessary substitutions in the subsequent commands.
Save Command
The save command stores the lidarscan and the lidar movement trajectory into a OSF file by
specifying a filename with a .osf extension. This OSF file will be used for accumulated point
cloud generation and the other post-process tools we offer in the future.
ouster-cli source <SENSOR_HOSTNAME> / <FILENAME> slam save sample.osf
The save command can also be used to generated an accumulated point cloud map using a
SLAM-generated OSF file in LAS (.las), PLY (.ply), or PCD (.pcd) format.
The output format depends on the extension of the output filename.
For example, to convert the OSF file we generated using the slam command to PLY format,
we can simply use the following:
ouster-cli source sample.osf save output.ply
You can utilize the slam command with the save command to directly generate a cumulative
point cloud map. However, please be aware that this combined process can be resource-intensive.
We recommend using this approach with a PCAP/OSF file rather than with a live sensor to avoid
SLAM performance degradation.
ouster-cli source <FILENAME> slam save output.ply
The accumulated point cloud data is automatically split and downsampled into multiple files to prevent exporting a huge size file. The terminal will display details, and you will see the following printout for each output file:
Output file: output-000.ply
Point Cloud status info
3932160 points accumulated during this period,
1629212 down sampling points are removed [41.43 %],
2213506 out range points are removed [56.29 %],
89442 points are saved [2.27 %]
Use the --help flag for more information such as selecting different fields as values,
and changing the point cloud downsampling scale etc.
To filter out the point cloud, you can using the clip command. Converting the SLAM output OSF
file to a PLY file and keep only the point within 20 to 80 meters range you can run:
ouster-cli source sample.osf clip --min-range 20 --max-range 80 save clipped_output.ply
More details about the clip command usage can be found in the Clip Command
You can use an open source software CloudCompare to import and view the generated point cloud data files.
Viz Command
The viz command enables visualizing the accumulated point cloud generation during the
SLAM process. By default, the viz operates in looping mode, meaning the visualization will
continuously replay the source file.
ouster-cli source <SENSOR_HOSTNAME> / <FILENAME> slam viz
When combining the viz and save commands, the saving process will automatically terminate
after the first iteration, and then the SLAM process restarts for each subsequent lidar scan iteration.
To end the SLAM and visualization processes after the save operation completes, you can use ctrl + c.
Alternatively, you can add -e exit to the viz command to terminate the process after a
complete iteration.
ouster-cli source <SENSOR_HOSTNAME> / <FILENAME> slam viz -e exit save sample.osf
Scans Accumulation: The viz command allows the user to customize …
Available view modes
There are three view modes of ScansAccumulator, that may be enabled/disabled depending on its params and the data that is passed through it:
poses (or TRACK), key
8- all scan poses in a trajectory/path view (available only if poses data is present in scans)scan map (or MAP), key
7- overall map view with select ratio of random points from every scan (available for scans with/without poses)scan accum (or ACCUM), key
6- accumulated N scans (key frames) that is picked according to params (available for scans with/without poses)
Key bindings
Keyboard controls available with ScansAccumulator:
Key
What it does
6Toggle scans accumulation view mode (ACCUM)
7Toggle overall map view mode (MAP)
8Toggle poses/trajectory view mode (TRACK)
k / KCycle point cloud coloring mode of accumulated clouds or map
g / GCycle point cloud color palette of accumulated clouds or map
j / JIncrease/decrease point size of accumulated clouds or map
Ouster CLI ScansAccumulator options:
--accum-num INTEGERAccumulate up to this number of past scans for visualization. Use <= 0 for unlimited. Defaults to 100 if--accum-everyor--accum-every-mis set.
--accum-every INTEGERAdd a new scan to the accumulator every this number of scans.
--accum-every-m FLOATAdd a new scan to the accumulator after this many meters of travel.
--mapIf set, add random points from every scan into an overall map for visualization. Enabled if either--map-ratioor--map-sizeare set.
--map-ratio FLOATFraction of random points in every scan to add to overall map (0, 1]. [default: 0.01]
--map-size INTEGERMaximum number of points in overall map before discarding. [default: 1500000]
Dense accumulated clouds view (with every point of a scan)
To obtain the densest view use the --accum-num N --accum-every 1 params where N is the
number of clouds to accumulate (N up to 100 is generally small enough to avoid slowing down
the viz interface):
ouster-cli source <SENSOR_HOSTNAME> / <FILENAME> slam viz --accum-num 20 save sample.osf
and the dense accumulated clouds result:

Dense view of 20 accumulated scans during the slam viz run
Overall map view (with poses)
One of the main tasks we frequently need is a preview of the overall map. We can test this by using
the SLAM-generated OSF file, which was created with the above command and contains the
SLAM trajectory in LidarScan.pose. If you are using a SLAM-generated OSF, you can directly use
viz with scan accumulator feature without appending the slam option.
ouster-cli source sample.osf viz --accum-num 20 \
--accum-every-m 10.5 --map -r 3 -e stop
Here is a preview example of the overall map generated from the accumulated scan results. By utilizing the ‘-e stop’ option, the visualizer stops once the replay process finishes, displaying the preview of the lidar trajectory:
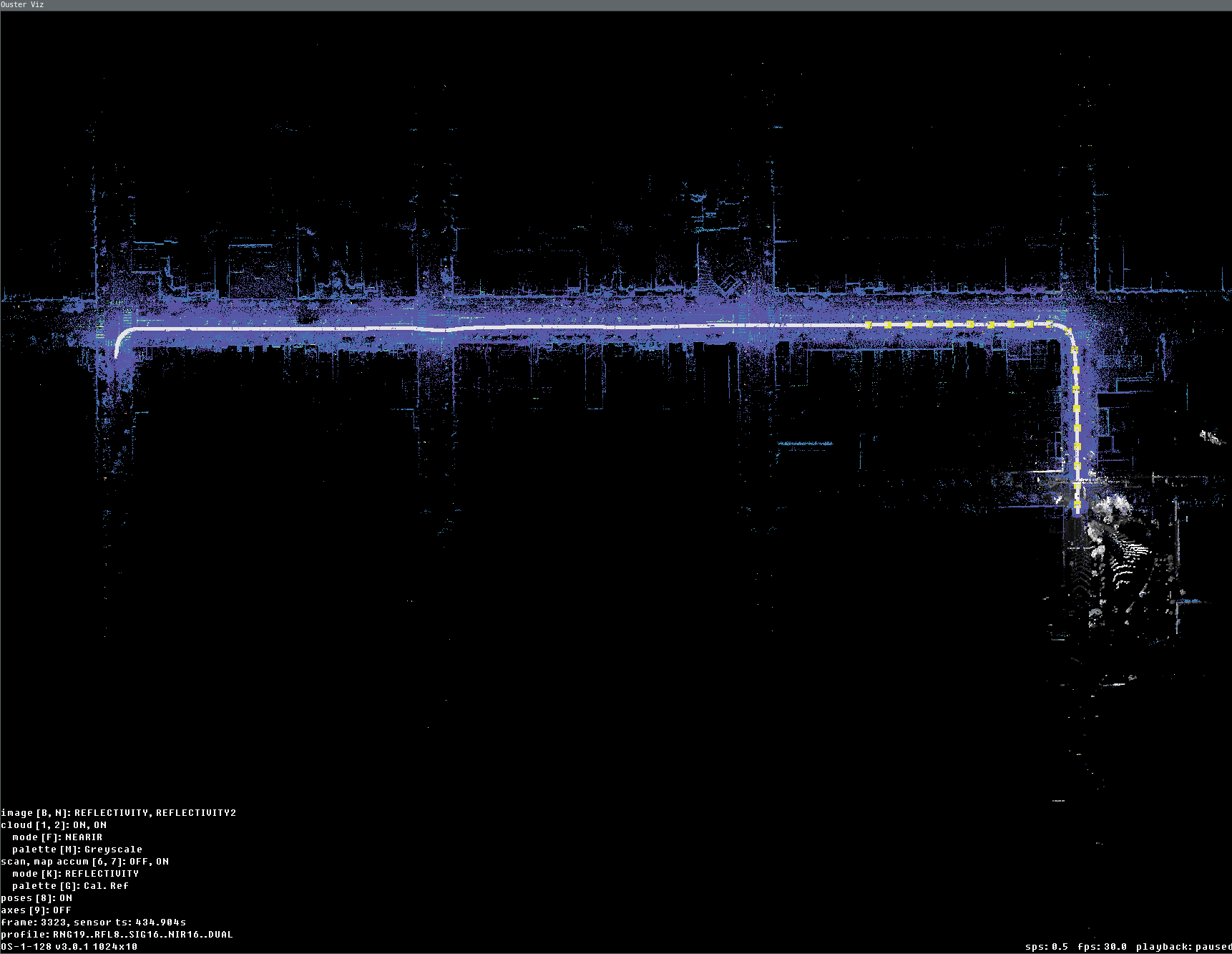
Data fully replayed with map and accum enabled (last current scan is displayed here in gray palette)